It’s the time of year for saving money!

J. Gordon Holt’s Audio
Glossary defines bloom as “a quality
of expansive richness and warmth, like the live body sound of a cello.” And
while I’ve certainly heard speakers that emphasize or restrict bloom, I’m not
familiar with a digital audio product functioning entirely in
the digital domain that alters a recording’s bloom. Analog electronics? Sure. And
in pro audio there’s a bunch of devices whose sole function is “fattening,”
such as Pultec EQs.
I bring this up
because I’ve seen quite a few reviews lately that make a big thing of the superior
“bloom” from one digital device over another. Now, I would never say or write,
“That’s BS!” when a reviewer goes off on a “bloom” tangent. But, I can’t help
but wonder about the methodology used to determine that one digital component
had more bloom than another.
For me a proper comparison set-up must have several key elements
to be useful. First and foremost a listener must have some means to accurately
match output levels between the two components. I use steady-state 1kHz and 500
Hz test tones to match levels when I’m doing an A/B comparison. And oftentimes
the initial set-up takes far longer than the actual A/B test.

Preamps or gain control devices that have numerical scales are
easier to use in an A/B test than preamps without a numbered volume system.
Ever try matching a volume levels consistently without some way to quantify
those levels? Not easy, and sometimes downright impossible. Recently I spent
time with three DSD DACs for an upcoming review for The Absolute Sound. Two of
them – the Mytek 192/24 DSD DAC and the Lynx Hilo, had numerically calibrated
and numbered volume controls, making the set-up for A/B tests fairly simple. In
contrast the Benchmark HGC DAC2, with its rotary, uncalibrated volume knob was
nowhere near as easy to set up for robust (the term for repeatable) A/B tests,
to the point where A/B tests using the DAC 2 were not useful.
Once levels are matched, the next most important detail in an
A/B comparison is a changeover from A to B that takes less than ten seconds.
While some audiophiles claim to have an aural recall ability that is so finely
tuned that they can take several minutes between changeovers, I can’t do an A/B
that has that kind of “lag time” between A and B and get consistent results.
Unless I can do a direct comparison within a short period of time, I can’t call
it an A/B, instead it’s more like X/A, X/A, X/A, which won’t tell you much.
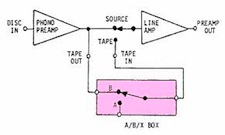
Those who are firmly in the A/B/X camp are wondering why I
don’t just use an ABX switchbox for my A/B tests. The reason is simple – an ABX
box adds too much extra stuff to the signal chain. The added relay contacts,
cable, terminations, and potential impedance changes caused by placing an ABX
box in the signal chain reduces a system’s overall fidelity and resolution by
just enough that very small differences can be lost. Instead of a straight A/B,
with no added stuff in the signal chain, we have an A/B that is no longer a
true A/B because of the ABX box. By using an ABX box for A/Bs, the only thing
you can say with absolute confidence if you don’t hear any difference between A
and B is that there was no audible difference between components WITH the ABX
box in the circuit. That is a far cry from stating that there was no difference
without the box.
But, back to room bloom. A good digital recording of an
acoustic musical event will very likely have instrument bloom, where an
individual instrument’s dynamics seem to expand, contract and breathe. But a
room-based stereo’s overall image should not “bloom.” This kind of bloom, where
above a certain SPL level the overall image size expands, is more a function of
room interactions than part of the original signal. And any system whose
imaging changes based on overall SPLs isn’t performing in a neutral and
balanced manner.

To sum up, if you notice added “bloom” when comparing one
digital device to another, don’t assume that the device with more bloom is
better or even that the bloom you are hearing is being caused by a particular
digital device. First you have to ascertain that the bloom is actually coming
from the digital source component and not merely from downstream components or your
room. For me the best way to figure this out that out is by constructing a robust
and repeatable A/B comparison. I only wish that all reviewers, amateur and
professional, would do the same.